The medium of exchange properties
A good medium of exchange is a form of currency that is widely accepted in transactions for goods and services. Some of the properties that make a good medium of exchange are:
- Acceptability: It should be accepted by a large number of people, businesses, and organizations.
- Divisibility: It should be easily divisible into smaller units so that it can be used to purchase items of any price.
- Durability: It should be resistant to wear and tear and not easily damaged.
- Transportability: It should be easy to transport and store.
- Limited Supply: Its supply should be limited to maintain its value.
- Unforgeability: It should be difficult to counterfeit or duplicate.
- Utility: It should be useful in itself or be readily exchangeable for goods and services.
In general, a good medium of exchange should have the following characteristics: it should be widely accepted, easily transportable, durable, and have a limited supply to maintain its value.
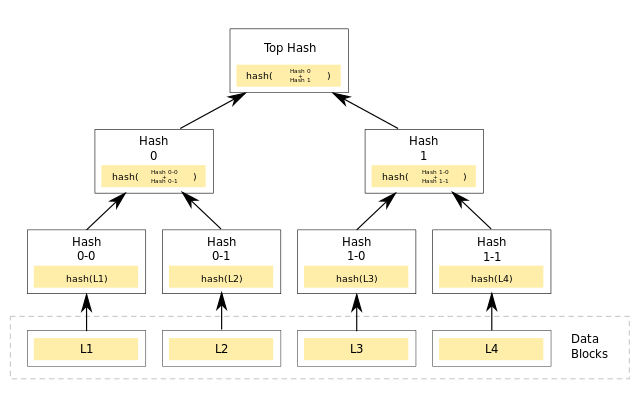
The Merkle tree
A Merkle tree, also known as a hash tree, is a data structure that is used to verify the integrity of data in a decentralized system. It allows for efficient and secure verification of large amounts of data.
In a Merkle tree, data is stored in a hierarchy of leaf nodes and intermediate nodes. Each leaf node contains a hash of some data, and each intermediate node contains the hash of the combination of its child nodes. This creates a tree-like structure with a single root node, which represents the top of the tree.
The advantage of a Merkle tree is that it allows for efficient verification of the data stored in the leaf nodes. If the root node of the tree is transmitted to a verifier, the verifier can then compute the hashes of the child nodes and compare them to the hashes transmitted along with the root node. If the hashes match, the verifier can be confident that the data in the leaf nodes has not been altered.
Merkle trees are widely used in decentralized systems, such as blockchain networks, to ensure the integrity of data stored on the network. They are also used in other systems, such as version control systems, to verify the integrity of large data sets.
What Is SHA-256 And How Is It Related to Bitcoin?
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit) is a cryptographic hash function that is widely used to verify the integrity of data. It produces a fixed-size output (256 bits) for any input data, regardless of the size or length of the input. The output of a SHA-256 hash function is often represented as a hexadecimal string of 64 characters.
SHA-256 is related to Bitcoin in that it is used in the mining process to secure the blockchain and verify transactions. In Bitcoin, transactions are grouped into blocks and added to the blockchain. Miners compete to solve a complex mathematical problem, and the first miner to solve the problem gets to add the next block to the blockchain.
To solve the mathematical problem, miners must produce a hash of the block that meets certain criteria. Specifically, the hash must be less than a target value that is determined by the network. This process is known as “mining” because it requires a lot of computational power and resembles the process of mining for gold.
The SHA-256 function is used to produce a hash of the block data. The miner must then find a nonce (a random number) that, when combined with the block data, produces a hash that meets the criteria set by the network. This process is very computationally intensive and requires a lot of trial and error. Once a miner finds a valid nonce, the block is added to the blockchain and the miner is rewarded with a certain number of bitcoins.
The "Blockchain"
In a blockchain, each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, along with data such as transactions. This creates a chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain.” Each block in the chain is linked to the one before it and after it, making it difficult to alter any previous block without also having to alter all subsequent blocks. This is what makes the blockchain model secure and resistant to tampering. The previous hash block is added to the new block as a reference and it’s a way to ensure the integrity of the blockchain, making sure that no one can change the previous blocks without being noticed.
In the Bitcoin network, nodes follow the longest valid chain of blocks. This is known as the “longest chain rule.” When two nodes have different versions of the blockchain, the one with the most blocks is considered to be the correct one. This is because it is computationally expensive to add blocks to the blockchain, so the chain with the most blocks is considered to have the most computational power behind it, and is therefore the most secure.
Nodes constantly receive new blocks from other nodes, and when a block is received, it is verified for validity. If the block is valid, the node will add it to its local copy of the blockchain and broadcast the block to other nodes. If the block is invalid, it is ignored.
This process ensures that the blockchain is decentralized and resistant to tampering. Since no single node controls the network, it is difficult for any one node to control which chain of blocks is considered to be valid. Instead, the network as a whole reaches consensus on which chain is valid.
How bitcoin wallets and keys are generated ?
A Bitcoin wallet is a software program that allows you to store, send, and receive Bitcoin. It consists of a public address and a private key.
The public address is a string of characters that represents the destination for a Bitcoin payment. It is similar to a bank account number or an email address. It can be shared with anyone who wants to send you Bitcoin.
The private key, on the other hand, is a secret password that is used to access and control the Bitcoin stored at the public address. It is similar to the PIN code on a debit card. The private key must be kept secret at all times, as anyone who has access to it can use it to spend the Bitcoin stored at the corresponding public address.
There are different types of Bitcoin wallets, including software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets.
Software wallets are programs that you install on your computer or mobile device. They provide the ability to create, store, and manage your public and private keys.
Hardware wallets are physical devices that store your private keys in a secure manner. They are often considered to be the most secure type of wallet because the private keys are stored offline and are not vulnerable to hacking.
Paper wallets are physical documents that contain the public and private keys. They can be printed out or stored as a digital file. Paper wallets are considered to be very secure because the private key is not stored on a computer or other device that is connected to the internet.
To generate a Bitcoin wallet and keys, you can use a software wallet or a hardware wallet. Some wallets will allow you to create a new wallet and keys when you install the software or set up the hardware device. Others may require you to create a new wallet and keys manually.
Regardless of the method you use, the process of generating a wallet and keys typically involves the following steps:
- Choose a wallet type: Decide which type of wallet you want to use (software, hardware, or paper).
- Install or set up the wallet: Follow the instructions for your chosen wallet to install the software or set up the hardware device.
- Create a new wallet: If required, create a new wallet and name it.
- Generate a public address and private key: The wallet will generate a public address and a private key for you. The private key should be kept secret at all times.
- Write down or save the keys: It is important to write down or save the keys in a secure location, as they are needed to access and control the Bitcoin stored at the corresponding public address.
- Secure the wallet: Follow the instructions for your wallet to secure it with a password or other security measures.
How Bitcoin offer you sovereignty and safety?
Bitcoin offers sovereignty and safety in several ways:
- Sovereignty: Bitcoin allows you to be in control of your own money. You are not subject to the policies or control of a central authority or financial institution. This means you have the freedom to send and receive payments, store your assets, and make financial decisions without interference.
- Safety: Bitcoin uses a decentralized, distributed ledger technology called the blockchain to secure and verify transactions. Each transaction is recorded on multiple copies of the ledger, which are stored on computers all over the world. This makes it virtually impossible for transactions to be altered or forged.
- Anonymity: Bitcoin allows you to transact anonymously, as you do not need to provide personal information in order to open a wallet or make a payment. This can protect your privacy and reduce the risk of identity theft.
- Security: Bitcoin uses strong encryption to secure the wallet and protect against hacking. It is important to choose a secure wallet and to follow best practices for keeping your private keys safe, such as using a strong password and enabling two-factor authentication.
Overall, Bitcoin offers users a high level of sovereignty and safety by allowing them to be in control of their own assets and providing strong security measures to protect against fraud and hacking.
Bitcoin is different from the current monetary system in several ways, particularly in terms of inflation and the storage of value.
- Inflation: Most national currencies, including the U.S. dollar, are subject to inflation. This means that the purchasing power of the currency decreases over time due to an increase in the supply of money. In contrast, Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, which limits the potential for inflation. The limited supply of Bitcoin is intended to maintain its value over time and make it a better store of value.
- Storage of value: Traditional assets such as gold and silver have been used as stores of value for centuries. These assets tend to hold their value over time, as they are scarce and have practical uses. Bitcoin can also be considered a store of value, as it has a limited supply and is accepted as a form of payment by an increasing number of merchants and organizations.